Best Urinary Bladder Treatment in Kolkata
Urinary bladder health is a fundamental aspect of overall well-being, and finding top-notch care is essential when facing bladder issues. In the bustling city of Kolkata, individuals have access to a wealth of expertise and specialized treatments for urinary bladder conditions. This guide is your key to understanding the importance of bladder health and discovering the best options for care and treatment available in Kolkata. Whether you’re seeking solutions for urinary tract infections, bladder stones, or more complex conditions like bladder cancer, Kolkata has dedicated professionals and advanced resources to support your journey towards better urinary bladder health. Let’s explore the world of urinary bladder care in the vibrant city of Kolkata, where expertise meets compassion to ensure your well-being. Plus, meet Dr. Nilanjan Mitra, the Best Urologist and Andrologist in Kolkata, for personalized care and top-notch expertise
Pediatric Bladder Conditions
Pediatric bladder conditions require specialized care to address the unique needs of children. Urologists who focus on pediatric urology are skilled in diagnosing and treating bladder issues in young patients. Common pediatric bladder conditions include:
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): UTIs can occur in children and may be indicative of underlying issues. Pediatric urologists assess and treat UTIs in children to prevent complications.
- Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR): This condition involves the abnormal flow of urine from the bladder into the ureters and can lead to recurrent UTIs. Pediatric urologists may recommend interventions like surgical correction.
- Bladder Dysfunction: Some children may experience bladder dysfunction, such as overactive bladder or underactive bladder. Treatment options may include behavioral therapy, medications, or biofeedback.
- Hydronephrosis: Hydronephrosis is the swelling of the kidney due to urine buildup. Pediatric urologists evaluate the cause of hydronephrosis and provide appropriate treatment.
- Congenital Anomalies: Urologists address congenital anomalies like posterior urethral valves, bladder exstrophy, and cloacal anomalies in pediatric patients through surgical and medical management.
- Bedwetting (Nocturnal Enuresis): Bedwetting is a common issue in children. Pediatric urologists can determine if underlying factors are contributing to bedwetting and offer interventions.
- Voiding Dysfunction: Pediatric urologists assess and manage voiding dysfunction issues that can affect a child’s ability to empty their bladder properly.
It’s important for parents to seek timely medical care from pediatric urologists when they suspect or notice bladder-related issues in their children. Early diagnosis and intervention can prevent long-term complications.
Female Urology Services
Female urology is a specialized field within urology that focuses on addressing urological conditions specific to women. Women may experience bladder and urinary tract issues that require the expertise of female urologists. Some key aspects of female urology services include:
- Pelvic Organ Prolapse: Female urologists diagnose and treat pelvic organ prolapse, a condition where pelvic organs, including the bladder, uterus, or rectum, descend into the vaginal canal. Treatment options include pelvic floor exercises, pessaries, or surgery.
- Urinary Incontinence: Female urologists provide comprehensive evaluation and treatment for urinary incontinence, which can occur due to stress, urge, or mixed incontinence. Treatment may include behavioral therapy, medications, or surgical procedures.
- Interstitial Cystitis (Bladder Pain Syndrome): Women are more commonly affected by interstitial cystitis, a chronic bladder condition characterized by pelvic pain and urgency. Female urologists offer specialized care and treatment options tailored to women.
- Recurrent UTIs: Women are prone to recurrent urinary tract infections. Female urologists can help identify risk factors and provide strategies for prevention.
- Pelvic Pain: Female urologists evaluate and manage pelvic pain conditions, which can have a significant impact on a woman’s quality of life.
- Voiding Dysfunction: Female urologists address issues related to voiding dysfunction, helping women achieve better bladder control.
- Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation: Pelvic floor physical therapy, a non-invasive approach, is often recommended by female urologists to improve pelvic muscle strength and function.
Choosing a female urologist can provide women with specialized care that considers their unique anatomical and physiological factors.
Male Bladder Health
While urology services cater to both men and women, men may encounter specific bladder health issues that require attention. Some aspects of male bladder health include:
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): BPH is a common condition in aging men where the prostate gland enlarges and can obstruct urine flow. Urologists offer various treatments, including medications and surgical procedures like TURP or laser therapy.
- Prostate Health: Urologists play a central role in assessing and managing prostate health, including monitoring for prostate cancer through screenings like the PSA test.
- Bladder Outlet Obstruction: Conditions like urethral strictures or bladder neck contractures can lead to bladder outlet obstruction in men. Urologists perform procedures to alleviate obstructions and improve urine flow.
- Bladder and Prostate Cancer: Urologists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of bladder and prostate cancers. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy.
- Male Voiding Dysfunction: Urologists evaluate and treat voiding dysfunction issues in men, including urinary retention or difficulty emptying the bladder.
- Erectile Dysfunction: While primarily addressed by urologists specializing in sexual health, bladder health can be affected by erectile dysfunction. Comprehensive care may involve both aspects.
- Fertility Concerns: Male fertility issues can impact reproductive health. Urologists can assess and treat conditions affecting sperm production and transport.
For men experiencing bladder-related symptoms, consulting a urologist is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Incontinence Treatment
Urinary incontinence, the involuntary loss of urine, can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Urologists offer various treatment options, tailored to the type and severity of incontinence:
- Behavioral Therapy: Urologists may recommend behavioral interventions, including bladder training, timed voiding, and fluid management strategies, to improve control.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: Kegel exercises, designed to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, can help manage incontinence, particularly in women.
- Medications: Depending on the type of incontinence, urologists may prescribe medications such as anticholinergics or beta-3 adrenergic agonists.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Urologists perform minimally invasive procedures like the injection of bulking agents or the placement of a urethral sling to provide support to the bladder neck.
- Artificial Urinary Sphincter (AUS): For severe cases of incontinence, urologists may recommend the implantation of an AUS, a device that provides control over urination.
- Botox Injections: In some cases, Botox injections into the bladder wall can help relax the bladder and improve control.
- Neuromodulation: Urologists may consider neuromodulation techniques, such as sacral neuromodulation, to regulate nerve signals related to bladder function.
- Surgical Options: For complex cases or when other treatments are ineffective, surgical procedures like urinary diversion or bladder augmentation may be considered.
It’s important to consult with a urologist to determine the underlying cause of incontinence and explore the most suitable treatment approach.
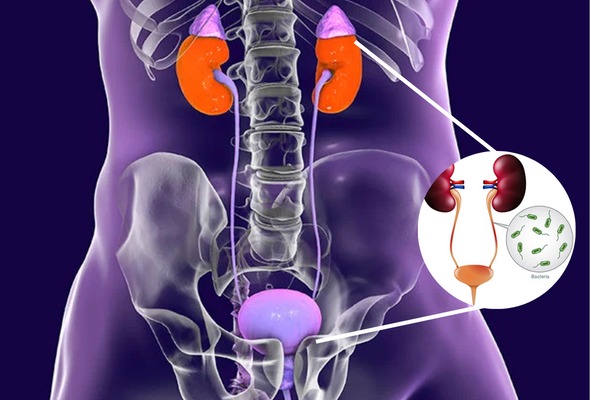
Bladder and Kidney Function
The bladder and kidneys are closely connected in the urinary system. Understanding their functions and the relationship between them is essential for managing urinary health.
- Bladder Function: The primary function of the bladder is to store urine until it is ready to be expelled from the body. Bladder muscles contract to push urine into the urethra during urination.
- Kidney Function: The kidneys filter waste products and excess substances from the blood to form urine. They play a vital role in maintaining the body’s overall fluid balance and electrolyte levels.
- Role of the Ureters: The ureters are tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder, allowing urine to flow from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder-Kidney Connection: Problems in the bladder, such as urinary retention or frequent infections, can impact kidney function. Conversely, kidney conditions can affect bladder health.
- Hydronephrosis: Obstruction of urine flow from the kidneys can lead to hydronephrosis, a condition characterized by kidney swelling. Urologists diagnose and treat the underlying causes to relieve hydronephrosis.
- Bladder-Kidney Imaging: Advanced imaging techniques, like MRI or CT scans, help urologists assess the bladder and kidneys for abnormalities or diseases.
Maintaining the health of both the bladder and kidneys is vital for overall well-being, and urologists play a pivotal role in diagnosing and treating conditions that affect these organs.
Minimally Invasive Bladder Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery has revolutionized urology, providing patients with less invasive options for treating bladder conditions. These techniques offer several advantages:
- Smaller Incisions: Minimally invasive procedures involve small incisions, resulting in less post-operative pain, reduced scarring, and quicker recovery times.
- Faster Recovery: Patients typically experience shorter hospital stays and a quicker return to their normal activities compared to traditional open surgery.
- Lower Risk of Complications: Minimally invasive procedures are associated with a lower risk of complications such as infection and bleeding.
- Precision: Advanced technology allows urologists to perform precise surgical maneuvers with improved visualization.
- Various Conditions: Minimally invasive techniques are applicable to a range of bladder conditions, including bladder cancer, stone removal, and urinary incontinence.
Examples of minimally invasive bladder surgeries include laparoscopic surgery and robotic-assisted surgery. These approaches are employed based on the patient’s condition and the urologist’s expertise.
Robotic Surgery for Bladder Issues
Robotic-assisted surgery, often performed with the da Vinci Surgical System, has become a valuable tool in urology, particularly for complex bladder surgeries. Key aspects of robotic surgery for bladder issues include:
- Enhanced Precision: Robotic systems offer a high degree of precision and control, allowing urologists to perform intricate maneuvers.
- 3D Visualization: Surgeons benefit from 3D high-definition visualization, providing a detailed view of the surgical site.
- Small Incisions: Robotic surgery involves small incisions, resulting in less trauma to surrounding tissues and improved cosmetic outcomes.
- Reduced Blood Loss: The fine control offered by robotic instruments can minimize blood loss during surgery.
- Shorter Hospital Stays: Patients undergoing robotic surgery often experience shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times.
- Applications: Robotic surgery is used in various bladder procedures, including bladder cancer removal, neobladder reconstruction, and prostatectomy for cancer involving the bladder.
Patients considering robotic surgery should consult with their urologist to determine if it’s an appropriate option for their specific condition.
Bladder Reconstruction Procedures
Bladder reconstruction procedures are performed to address issues like bladder cancer, trauma, or congenital abnormalities. These procedures aim to restore or enhance bladder function and may include:
- Neobladder Reconstruction: In cases where the bladder must be removed due to cancer or other reasons, a neobladder may be created. A neobladder is a surgically constructed bladder substitute that allows for urine storage and release. This procedure requires specialized urological expertise.
- Bladder Augmentation: Bladder augmentation involves increasing the size of the bladder by using a segment of the patient’s intestine. This can be beneficial for individuals with small bladder capacities or those who have undergone bladder removal.
- Ileal Conduit: In situations where the bladder cannot be preserved, an ileal conduit diversion may be performed. This involves redirecting urine from the kidneys to a stoma on the abdomen, where a pouch or bag is attached to collect urine.
- Continent Diversion: Continent diversion procedures create a way for patients to store urine internally without the need for an external bag. Examples include the Indiana pouch and the Kock pouch.
- Bladder Substitution: For certain medical conditions, a bladder substitution surgery may be necessary, involving the removal of the bladder and the creation of an alternative urinary reservoir, such as a continent cutaneous reservoir.
These complex procedures require careful planning and expertise in bladder reconstruction. Urologists work closely with patients to determine the most appropriate reconstruction option based on their individual needs and medical history.
Cystoscopy and Urodynamic Studies
Diagnostic tools like cystoscopy and urodynamic studies are valuable for assessing bladder function and diagnosing various bladder conditions.
- Cystoscopy: Cystoscopy is a procedure in which a thin, flexible tube with a camera (cystoscope) is inserted into the urethra to visualize the inside of the bladder. It allows urologists to identify abnormalities, such as tumors, strictures, or bladder stones.
- Urodynamic Studies: Urodynamic studies involve a series of tests to assess how well the bladder, urethra, and sphincters are functioning. These tests are particularly useful in diagnosing urinary incontinence and voiding dysfunction.
- Cystometry: Cystometry measures the pressure inside the bladder during filling and emptying. It helps evaluate bladder capacity and assesses involuntary contractions.
- Pressure Flow Studies: Pressure flow studies determine the pressure and flow rate of urine during voiding, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions like bladder outlet obstruction.
- Electromyography (EMG): EMG measures the electrical activity of the pelvic floor muscles, helping to assess neuromuscular function related to bladder control.
- Video Urodynamics: This combines cystoscopy with urodynamic studies, allowing for simultaneous visualization of the bladder’s interior and measurement of its function.
Cystoscopy and urodynamic studies provide urologists with valuable information to diagnose bladder conditions accurately and develop appropriate treatment plans.
Advanced Imaging for Bladder Diagnosis
Advanced imaging techniques play a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring bladder conditions. These methods provide detailed views of the bladder and surrounding structures:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the bladder and nearby tissues. It is particularly useful for evaluating bladder cancer staging and assessing structural abnormalities.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: CT scans can provide cross-sectional images of the bladder, helping identify tumors, stones, or other abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging is non-invasive and can be used to visualize the bladder and assess urinary retention, bladder wall thickness, and the presence of stones.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan: PET scans with a radiotracer are sometimes used to detect and stage bladder cancer.
- Fluoroscopy: Fluoroscopy is a real-time X-ray imaging technique used during procedures like voiding cystourethrography (VCUG) to assess bladder function and urinary reflux.
- Nuclear Medicine Imaging: Radioactive tracers can be used in nuclear medicine studies to assess kidney and bladder function, particularly in cases of suspected obstruction.
These advanced imaging modalities aid urologists in making precise diagnoses and treatment decisions.
Bladder Health and Aging
As individuals age, changes in bladder function are common. Understanding the impact of aging on bladder health is essential:
- Reduced Bladder Capacity: Aging can lead to a decrease in bladder capacity, resulting in the need for more frequent urination.
- Decreased Muscle Tone: Bladder muscles may lose tone over time, contributing to issues such as urinary incontinence.
- Increased Risk of UTIs: Older adults are more susceptible to urinary tract infections (UTIs) due to changes in immune function and hormonal fluctuations.
- Medications and Bladder Function: Some medications commonly prescribed to older adults can affect bladder function and contribute to urinary symptoms.
- Bladder Retention: Older adults may experience difficulty fully emptying the bladder, increasing the risk of urinary retention.
- Functional Changes: Age-related functional changes in the bladder can affect the ability to control urination.
- Management Strategies: Urologists and healthcare providers offer management strategies tailored to the specific needs of older adults, such as lifestyle modifications, medications, and incontinence products.
Maintaining bladder health in older age may involve addressing these age-related changes through appropriate interventions and regular check-ups with urologists.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Management
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition in aging men where the prostate gland enlarges, leading to urinary symptoms. Managing BPH involves a range of approaches:
- Watchful Waiting: For mild symptoms, a urologist may recommend watchful waiting, with regular monitoring and lifestyle modifications.
- Medications: Several medications are available to treat BPH, including alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, which can relieve symptoms and reduce prostate size.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Minimally invasive procedures like transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT) or prostate artery embolization (PAE) can provide relief for moderate BPH symptoms.
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): TURP is a surgical procedure to remove excess prostate tissue and improve urine flow.
- Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP): HoLEP is another surgical option that uses laser technology to remove prostate tissue.
- UroLift: UroLift is a minimally invasive procedure that places small implants in the prostate to lift and hold the enlarged tissue, improving urinary flow.
- Combination Therapy: In some cases, a combination of medications and minimally invasive procedures may be recommended.
BPH management aims to alleviate urinary symptoms and improve overall quality of life for affected individuals.
Urologic Oncology for Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is a significant concern, and urologic oncologists specialize in its diagnosis and treatment. The management of bladder cancer may involve multiple disciplines, including surgery, medical oncology, and radiation oncology. The treatment approach depends on various factors, such as the cancer stage, grade, and the patient’s overall health.
Common treatment modalities for bladder cancer include:
- Transurethral Resection: For early-stage bladder cancer, the tumor may be removed through a cystoscope. This procedure is known as transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT).
- Surgery: Depending on the stage of the cancer, surgical options may include partial or radical cystectomy (removal of part or all of the bladder), lymph node dissection, and urinary diversion procedures.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy may be used before or after surgery, or as the primary treatment for advanced bladder cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: In some cases, radiation therapy may be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy, especially when surgery is not an option.
- Immunotherapy: Immune checkpoint inhibitors have shown promise in treating advanced bladder cancer by stimulating the body’s immune system to target cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapies, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors, are being studied as potential treatments for bladder cancer.
- Clinical Trials: Patients with advanced or refractory bladder cancer may have access to clinical trials investigating novel treatments and therapies.
Bladder Health Education and Prevention
Preventing bladder issues and promoting bladder health are important aspects of urology care. Education and preventive measures include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Advising patients on lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, and avoiding smoking, can contribute to bladder health.
- Dietary Guidance: Urologists may provide dietary recommendations to minimize bladder irritation and promote good urinary tract health.
- Hygiene Practices: Educating patients on proper hygiene, including wiping from front to back to prevent UTIs, is crucial.
- Fluid Intake: Discussing appropriate fluid intake and avoiding excessive consumption of irritants like caffeine and alcohol can help prevent bladder issues.
- Kegel Exercises: Instructing individuals, especially women, on performing Kegel exercises can improve pelvic floor muscle strength and bladder control.
- Regular Checkups: Encouraging patients to schedule regular checkups with their urologist for early detection of potential issues.
- Awareness of Risk Factors: Informing patients about risk factors for bladder conditions, such as family history and exposure to certain chemicals, is essential.
Urinary Bladder Rehabilitation
Bladder rehabilitation programs are designed to help individuals with urinary incontinence and other bladder problems regain control and improve their quality of life. These programs typically include:
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: Pelvic floor muscle training, including Kegel exercises, can strengthen the muscles that control bladder function.
- Bladder Training: This technique involves scheduled voiding and gradually increasing the time between bathroom trips to improve bladder control.
- Biofeedback: Biofeedback therapy helps individuals gain awareness and control over their pelvic muscles and bladder function.
- Electrical Stimulation: Some individuals benefit from electrical stimulation of the pelvic floor muscles to improve bladder control.
- Behavioral Strategies: Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and fluid management, may be recommended as part of bladder rehabilitation.
- Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage overactive bladder or other bladder-related issues.
These programs are typically tailored to the individual’s specific needs and may involve a combination of these therapies.
Telemedicine for Bladder Consultations
Telemedicine has become increasingly important in healthcare, offering remote access to medical consultations and advice. Telemedicine for bladder consultations allows patients to connect with urologists from the comfort of their homes or local clinics. This can be especially valuable for follow-up appointments, routine checkups, or initial assessments of bladder concerns.
Telemedicine appointments typically involve videoconferencing with the urologist, during which the patient can discuss symptoms, receive guidance on treatment or management, and ask questions. In some cases, physical examinations or diagnostic tests may still be required, but the initial consultation and many follow-up discussions can be conducted remotely.
Bladder Health Research in Kolkata
Kolkata, as a center for medical research and healthcare, is home to various institutions and universities conducting research in urology and bladder health. Research in this field aims to advance our understanding of bladder conditions, improve diagnostic methods, develop new treatment options, and enhance patient outcomes.
Some areas of ongoing research in bladder health include:
- Genetics and Bladder Conditions: Investigating the genetic factors that predispose individuals to bladder diseases, such as interstitial cystitis and bladder cancer.
- Immunotherapy and Bladder Cancer: Advancing immunotherapy approaches for the treatment of bladder cancer, including the development of novel immunotherapeutic agents.
- Biomarker Discovery: Identifying biomarkers that can aid in the early diagnosis and monitoring of bladder conditions.
- Drug Development: Developing new medications and therapies for various bladder disorders, including overactive bladder and interstitial cystitis.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Researching innovative minimally invasive surgical techniques and robotic-assisted procedures to improve patient outcomes.
- Quality of Life Studies: Conducting studies to assess the impact of bladder conditions on patients’ quality of life and developing interventions to enhance their well-being.
Collaboration between researchers, urologists, and healthcare institutions in Kolkata contributes to advancements in urology and bladder health care.
Fertility Preservation in Bladder Patients
Preserving fertility is a significant concern for individuals undergoing bladder-related treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy. These treatments can potentially impact reproductive function. Fertility preservation options include:
- Sperm Banking: For men, sperm banking is a common method of preserving fertility before undergoing bladder or prostate surgeries.
- Egg Freezing: Women can opt for egg freezing (oocyte cryopreservation) to preserve their eggs before cancer treatments that may affect fertility.
- Embryo Cryopreservation: Couples can freeze embryos created through in vitro fertilization (IVF) for future use.
- Gonadal Shielding: In some cases, protective shields can be used during radiation therapy to minimize radiation exposure to the reproductive organs.
- Consultation with Fertility Specialists: It’s crucial for patients to consult with fertility specialists who can provide personalized guidance and options.
- Post-Treatment Fertility: After bladder treatment, individuals should discuss their fertility preservation options for future family planning with their healthcare team.
Second Opinion for Bladder Conditions
Seeking a second opinion is a valuable practice, especially for complex bladder conditions or when facing significant treatment decisions. Second opinions can provide patients with additional perspectives on their diagnosis and treatment options. Here are some key points to consider when seeking a second opinion:
- Confidence and Peace of Mind: A second opinion can provide reassurance and increase confidence in the chosen treatment plan.
- Treatment Alternatives: Another urologist may suggest alternative treatment options that were not initially considered.
- Understanding the Diagnosis: It can help patients gain a better understanding of their condition and its implications.
- Confirmation of Diagnosis: A second opinion can confirm the accuracy of the initial diagnosis, ensuring that no critical details are overlooked.
- Treatment Risks and Benefits: It allows patients to compare the risks and benefits of different treatment approaches.
- Exploring Clinical Trials: In some cases, a second opinion may lead to the consideration of participation in clinical trials for novel treatments.
- Communication with Current Healthcare Team: It’s essential to communicate with the current healthcare team about seeking a second opinion. They can help facilitate the process.
In conclusion,
bladder health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being, and individuals in Kolkata have access to a range of specialized urologists and advanced medical services to address various bladder conditions. From diagnosis to treatment, the field of urology continues to evolve with advancements in technology and research, offering patients a diverse array of options to maintain or improve their bladder health. Seeking the expertise of top urologists, staying informed about bladder health, and considering second opinions when necessary can contribute to better outcomes and quality of life for individuals with bladder-related concerns.
Certainly! Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to the topics covered in the blog about bladder health, urology, and related medical services:
Best Urinary Bladder Treatment in Kolkata
1. What is a urologist, and when should I see one?
- A urologist is a medical specialist who diagnoses and treats conditions related to the urinary tract and male reproductive system. You should consider seeing a urologist if you experience symptoms such as frequent urination, blood in the urine, urinary incontinence, or any discomfort or pain in the pelvic region.
2. What are common bladder conditions, and how are they treated?
- Common bladder conditions include urinary tract infections (UTIs), bladder infections, overactive bladder, and interstitial cystitis. Treatment varies depending on the condition but may involve medications, lifestyle changes, physical therapy, or minimally invasive procedures.
3. What is the role of urologists in managing bladder cancer?
- Urologists play a critical role in diagnosing and treating bladder cancer. They perform procedures such as transurethral resection of bladder tumors (TURBT), partial or radical cystectomy, and administer intravesical chemotherapy or immunotherapy to manage the disease.
4. How can I prevent urinary tract infections (UTIs)?
- Prevent UTIs by staying hydrated, practicing good hygiene, urinating before and after sexual activity, and avoiding irritants like excessive caffeine and alcohol. If you’re prone to UTIs, consult a urologist for preventive strategies.
5. What are the treatment options for urinary incontinence?
- Treatment options for urinary incontinence include behavioral therapy, pelvic floor exercises, medications, minimally invasive procedures, and, in severe cases, surgical interventions like sling procedures or artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) placement.
6. How do aging and menopause affect bladder health in women?
- Aging can lead to reduced bladder capacity, weakened pelvic floor muscles, and increased susceptibility to urinary incontinence. Menopause can contribute to lower estrogen levels, which may impact bladder function. Pelvic floor exercises and hormonal therapy can help manage these changes.
7. What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), and how is it treated?
- BPH is an enlarged prostate gland common in older men. Treatment options include watchful waiting, medications, minimally invasive procedures like UroLift or TURP, and, in severe cases, surgical removal of excess prostate tissue.
8. How do robotic surgeries benefit patients with bladder issues?
- Robotic-assisted surgery offers improved precision, 3D visualization, smaller incisions, and faster recovery times. It is used for complex bladder surgeries like bladder cancer removal, neobladder reconstruction, and prostatectomy involving the bladder.
9. What is bladder reconstruction, and when is it necessary?
- Bladder reconstruction involves surgical procedures to restore or enhance bladder function. It may be necessary for conditions like bladder cancer, trauma, or congenital anomalies. Procedures include neobladder reconstruction, bladder augmentation, and urinary diversion.
10. What are the benefits of telemedicine for bladder consultations?
- Telemedicine allows patients to consult with urologists remotely, offering convenience, access to specialists, and the ability to discuss symptoms, treatment plans, and follow-up appointments without the need for in-person visits.
11. What research is being conducted in Kolkata related to bladder health?
- Kolkata is home to various medical institutions conducting research in urology and bladder health, focusing on genetics, immunotherapy, biomarker discovery, drug development, minimally invasive techniques, and quality of life studies for individuals with bladder conditions.
12. How can I preserve fertility when undergoing bladder-related treatments?
- Fertility preservation options include sperm banking for men and egg or embryo freezing for women. Consultation with fertility specialists before bladder-related treatments is essential to explore the most suitable options.
13. When should I seek a second opinion for bladder-related conditions?
- Consider seeking a second opinion for complex bladder conditions, treatment decisions, or when you want additional perspectives on your diagnosis. It can provide confidence and potentially reveal alternative treatment approaches.

